
Polymers can be produced from renewable sources or fossil fuel derivatives. This can come in the form of oil or starch from plants. The source raw material is generally referred to as feedstock and fed to the in the refineries or cracking units.
The feedstock is cracked into various fractions or distillates. The fractions to be used for polymer production are termed monomers or comonomers, an example being ethylene, or styrene or propylene and others. These derivatives are the building blocks of the polymer resins.
The Process involves the combination of monomers and co-monomers to form chains of molecules which can be long or short, branched or unbranched, depending on the natures of the monomers, co-monomers, catalyst, pressure, temperature and other factors. These make it possible to produce several variety of plastics exhibiting numerous physical and chemical properties.
Plastics are made by blending the polymer resins with additives to create daily articles, typically in the presence of heat and torque or pressure mainly by a process called extrusion. The incredible properties have enabled plastics gain wide acceptance and penetrated our daily lives from Medical artificial artery tubing, to national drinking water pipes, to our favourite smart phones, to insulations to reduce energy cost.
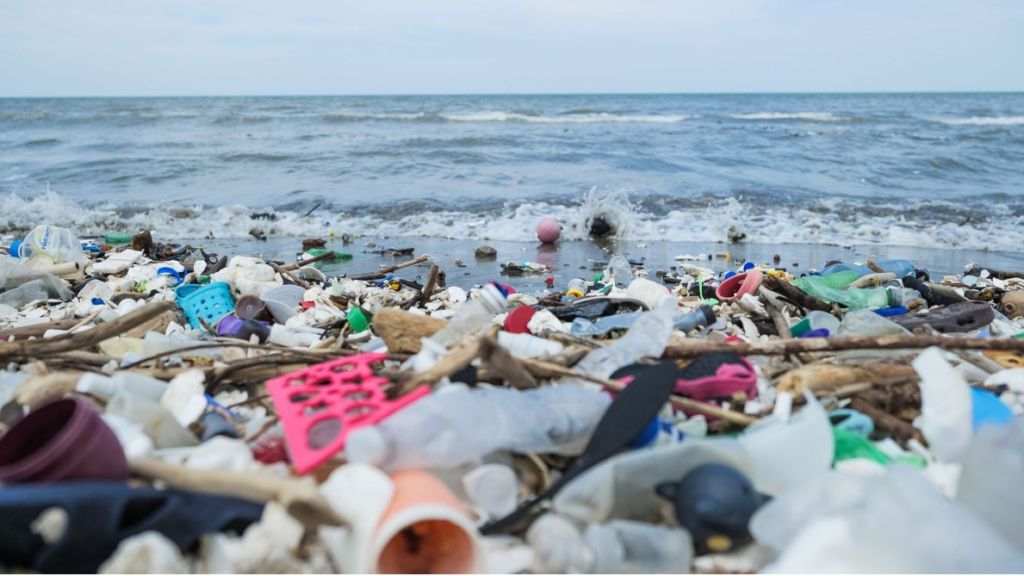
Plastic waste management is one of the world’s biggest challenges


Global
EU 27+3
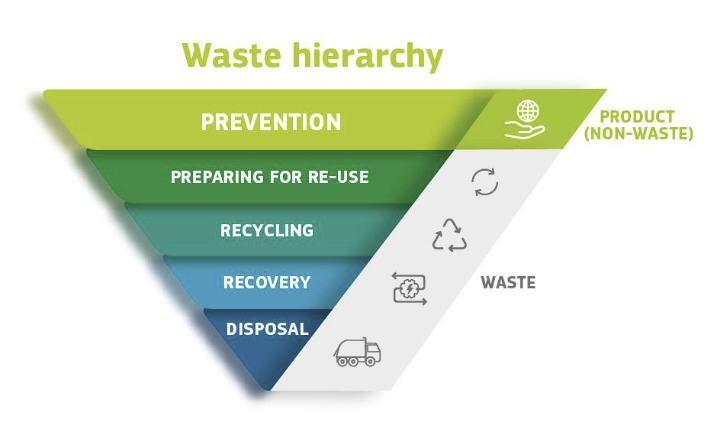
Internationally there’s a well adopted concept for plastic waste management which forms the pillar of Bluesalt. This entails a 4R principle contained in a 5 level inverse Pyramid according to the order of preference.
The idea behind this is to prioritize the higher level of the pyramid verses the one(s) below it.
Bluesalt advanced recycling solution will complement mechanical recycling and take volumes from recovery part of the pyramid (incineration and landfill).
Our SML technology delivers CO2 saving upto 70% vs incineration.
